Translocation t(12;15) (p13;q25) is a marker of several types of neoplasia. It is characteristically found in secretory breast carcinoma, congenital fibrosarcoma, cellular and mixed types of mesoblastic nephroma and also rarely in acute myeloid leukemia.
This translocation affects genes ETV6 (TEL) on the chromosome 12 and NTRK3 (TRKC) on the chromosome 15. The most often it comes to the breakage in the intron 5 of the gene ETV6 and the intron 12 of the gene NTRK3. This creates a fusion gene;or more precisely a protein, where there is N-terminal helix-loop-helix (HLH) domain of the highly expressed transcription factor ETV6 linked to tyrosine kinase domain of the gene NTRK3. The chimeric protein is subject to the ligand dependent HLH mediated dimerization with a subsequent activation of NTRK3 tyrosine kinase domain. The activated tyrosine kinase, then, through a number of signaling pathways, acts in the cell transformation.
Examination
We analyze the presence of the translocation t(12;15), better said the presence of the ETV6 gene breakage, by the use of RT-PCR and FISH.
RT-PCR
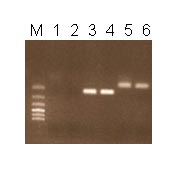
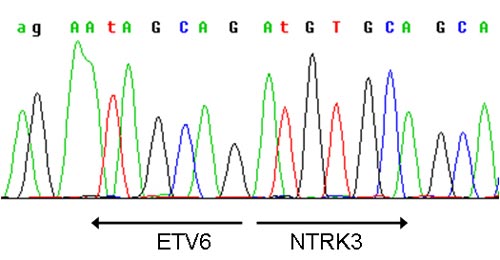
When RT-PRC we isolate mRNA and after its transcription into cDNA we detect chimeric transcripts by PCR. PCR products are visualized through the agarose gel electrophoresis (fig. 1) and positive samples are sequenced (fig. 2).
FISH
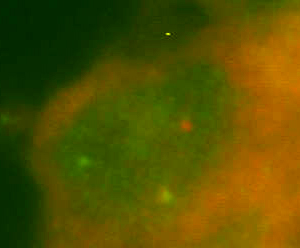
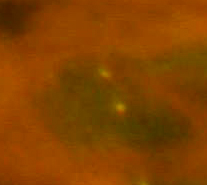
When FISH we detect the breakage of the gene ETV6 using ETV6 Dual Color, Break Apart Rearrangement Probe firm Vysis/Abbot (this probe does not identify a specific translocation partner. In the sample which is positive for rearrangement of the gene ETV6 we observe one yellow, one red and one green signal (fig. 3a). In the sample which is negative we observe two yellow signals (fig. 3b) (“dual color“ filter).
References
- Rubin BP, Chen CJ, Morgan TW, Xiao S, Grier HE, Kozakewich HP, Perez-Atayde AR, Fletcher JA. Congenital mesoblastic nephroma t(12;15) is associated with ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion: cytogenetic and molecular relationship to congenital (infantile) fibrosarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1998;153(5):1451-1458.
- Knezevich SR, McFadden DE, Tao W, Lim JF, Sorensen PH. A novel ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion in congenital fibrosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1998;18(2):184-18
- Tognon C, Knezevich SR, Huntsman D, Roskelley CD, Melnyk N, Mathers JA, Becker L, Carneiro F, MacPherson N, Horsman D, Poremba C, Sorensen PH. Expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion as a primary event in human secretory breast carcinoma.Cancer Cell. 2002;2(5):367-376.
- Bourgeois JM, Knezevich SR, Mathers JA, Sorensen PH. Molecular detection of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion differentiates congenital fibrosarcoma from other childhood spindle cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24(7):937-946.
- Pfeifer JD (Ed). Molecular Genetic Testing in Surgical Patology. LWW 2006. Philadelphia, USA.